- Home
- For the homeowner
- Safety
- Definitions
- Gas furnace
- Some error codes for gas furnaces
- Service sheet for the gas furnace
- gas furnace design
- The gas heat exchanger
- Dangerous conditions in gas furnaces
- Annual service of the gas furnace
- Repair procedures for gas furnaces
- Gas fireplace millivolt systems
- Oil furnace
- Setting gas input
- Quick tips for troubleshooting furnaces
- Troubleshoot
- Operation and troubleshoot furnace by manufacturer
- HVAC war stories blog
- Annual service of an oil furnace
- Oil furnace design
- Oil furnace troubleshoot
- Repair procedures for oil furnaces
- Gas code training
- Piping and connections
- FAG w pilot no fire
- Combustion analysis
- Electric furnace
- Air conditioner
- Refrigeration
- Heat Pump
- Boiler
- Ductwork design and troubleshoot
- Thermostats
- Diagnostic problems
- Tools
- Electric test meters
- Electrical diagram training
- Electrical symbols
- Single and 3 phase power systems
- Electric wiring solutions
- Transformer design and troubleshoot
- Electronic air cleaner
- Blowers and fans design & troubleshoot
- Humidity and humidifiers
- Furnace, Air Conditioner and part manuals
- Electric motors
- Run Capacitors
- Start capacitors
- Troubleshooting the capacitor
- Gas furnace short cycling
90+% furnace troubleshoot, power available to furnace, no heat
No burner ignition Click here
Burner stays on for a short time (4 to 7 seconds) Click here
Failure light codes Click here
Pressure switch problems Click here
Inducer or combustion fan problems
High temperature problems
Control board (IFC, brain board) problem below
This is an IFC
This control has a light on the lower left. It will blink a code to tell you the status of the control and furnace.
There is a key to the code blinks on the front of the control. |
This is another style IFC
This is essentially the same part. It does not have a plastic cover and the error code key is on one of the panels.
|
The controls on these furnaces are designed to blink a code to assist in troubleshooting.
The code will not always tell you exactly what is wrong, but will tell you the area in which to look.
When the furnace has a call for heat, the IFC begins a sequence of operation in order to safely start and operate the furnace. If at any time the IFC is not satisfied, the unit shuts down.
The code will not always tell you exactly what is wrong, but will tell you the area in which to look.
When the furnace has a call for heat, the IFC begins a sequence of operation in order to safely start and operate the furnace. If at any time the IFC is not satisfied, the unit shuts down.
90% furnace sequencing
1. On a call for heat (thermostat closes), a signal is sent to the IFC and sequencing begins.
2. The IFC electronically looks at the pressure switch.
A. If the pressure switch is open (power cannot pass through), the IFC starts the inducer.
B. If the pressure switch is closed (power passes through), sequencing stops and IFC goes into lockout mode. Lockout code will displayed on the IFC by blinking lights on the module. (key to codes should be listed on the furnace panel).
C. Most IFCs will attempt to try again 10 to 15 minutes later.
3. Once the inducer starts, the pressure switch should close.
A. If the pressure switch does not close, the inducer will continue to run for 1 to 2 minutes then will lockout and try again 10 to 15 minutes later.
B. If the pressure switch closes, the prepurge will begin.
4. The IFC will look at the limit switches.
A. If any of the limit switches are open, the furnace will lockout, the circulating fan will come on and a lockout code will be displayed.
B. If the limit switches are closed, the the warmup time for the HSI begins. A yellow glow will come from one side of the burner box.
5. The HSI warms for from 10 to 45 seconds.
6. The gas valve opens for 4 to 7 seconds to allow gas to pass into the burners. This is called the "trial for ignition"
7. If the burners ignite, the flame is proven, usually by flame rectification, during this time. The flame is sensed by a flame rod on the opposite side of the burners as the yellow glow. There should be a blue light in the burner box.
8. If the burners fail to ignite, the furnace shuts off the gas supply, goes through a purge cycle and attempts to light the burners again.
9. The furnace tries a total of 3 times, then if flame is not established goes into hard lockout. A lockout code will be displayed on the IFC.
10. After 1 hour, the furnace will start the entire sequence again to try to fire off.
11. If the flame is proved, a timer is started to delay the start of the circulating fan for 30 to 40 seconds.
12. When the call for heat is over, the burner extinguishes. The circulating fan continues to run for 2 to 3 minutes to clear heat from the heat exchanger.
13. This sequence is generic. Some furnaces will vary in their actual sequence, but will be substantially the same.
IFC failure codes
First, when troubleshooting problems with IFCs it is important to know that when there is a break in the sequence, the IFC will stop the attempt to start after a short time and go into lockout. With some of these actions, you will have only about 1 minute to troubleshoot the problem.
Pressure switch problem code: Here are some common IFC codes Pressure switch stuck closed
When there is a call for heat, the IFC checks to see if the pressure switch is open. If it is closed, the sequence stops and, after a short time, the pressure problem code is displayed.
If you get a pressure switch code, and the inducer will not come on, remove one of the wires from the pressure switch. If the inducer comes on, the pressure switch is stuck closed. Tapping lightly on the pressure switch body may open the switch and the unit may start. This is not a repair. The pressure switch must be replaced. Only OEM pressure switches should be used.
Pressure switch problem code: Here are some common IFC codes Pressure switch stuck closed
When there is a call for heat, the IFC checks to see if the pressure switch is open. If it is closed, the sequence stops and, after a short time, the pressure problem code is displayed.
If you get a pressure switch code, and the inducer will not come on, remove one of the wires from the pressure switch. If the inducer comes on, the pressure switch is stuck closed. Tapping lightly on the pressure switch body may open the switch and the unit may start. This is not a repair. The pressure switch must be replaced. Only OEM pressure switches should be used.
Limit switch codes
If your furnace failure code indicates an "open limit" or "open high temperature switch" or "open rollout switch", it is probable that the furnace has overheated. Some common limit switches are shown below.
The blower below could be the cause of limiting out of the furnace

This is the result of no filter in the furnace or a plugged filter.
It requires thorough cleaning by disassembly and cleaning the blower wheel with strong detergent or power wash. The motor (center) should not get water on it. Clean it with a brush.
For blower troubleshoot click here
It requires thorough cleaning by disassembly and cleaning the blower wheel with strong detergent or power wash. The motor (center) should not get water on it. Clean it with a brush.
For blower troubleshoot click here
Below are examples of a rollout switch (below left) and a limit switch (below right) as installed in the furnace.
If you see an error code for high temperature limit, usually limit switches and rollout switches are wired in series, so if one of the limits opens the burners will shut down.
The limit shown on the right senses the temperature inside the furnace. When it shuts off due to high temperature, you should check filter condition first. A dirty blower wheel could also be the problem.
This limit should reset on its own when the temperature returns to normal. Occasionally, the limit will not reset on its own. This is usually because the low air flow that caused the problem has continued for too long. The switch can be removed and struck against the furnace body lightly. This may break loose the contacts inside. If this solves the problem do not trust the switch not to fail again. Replace it.
The rollout switch on the left will not reset if it opens. The reason it will not reset is if it has opened, there is an unsafe condition in the furnace. It can be reset manually by pushing the button on the center. I do not recommend resetting the rollout switch without finding the reason for the failure. Rollout means the switch has been subject to high temperatures as in flame rolling out the front of the furnace. This could be due to a heat exchanger failure. The unit could also have been over fired. Either way, find out the problem before proceeding. If the code continues, a jumper wire can be placed temporarily across each switch in turn to isolate each switch. When you place a jumper across a limit, the power should be off. Then turn on the power and see if the unit starts.
If the unit starts, you have found the problem. DO NOT leave a jumper across any safety control permanently.
If all these tests fail to isolate the problem and the code continues, check all wiring connections for tight.
At this point the IFC appears to have failed. As the most expensive part of this part of the furnace, be sure all other parts have been thoroughly checked.
If you see an error code for high temperature limit, usually limit switches and rollout switches are wired in series, so if one of the limits opens the burners will shut down.
The limit shown on the right senses the temperature inside the furnace. When it shuts off due to high temperature, you should check filter condition first. A dirty blower wheel could also be the problem.
This limit should reset on its own when the temperature returns to normal. Occasionally, the limit will not reset on its own. This is usually because the low air flow that caused the problem has continued for too long. The switch can be removed and struck against the furnace body lightly. This may break loose the contacts inside. If this solves the problem do not trust the switch not to fail again. Replace it.
The rollout switch on the left will not reset if it opens. The reason it will not reset is if it has opened, there is an unsafe condition in the furnace. It can be reset manually by pushing the button on the center. I do not recommend resetting the rollout switch without finding the reason for the failure. Rollout means the switch has been subject to high temperatures as in flame rolling out the front of the furnace. This could be due to a heat exchanger failure. The unit could also have been over fired. Either way, find out the problem before proceeding. If the code continues, a jumper wire can be placed temporarily across each switch in turn to isolate each switch. When you place a jumper across a limit, the power should be off. Then turn on the power and see if the unit starts.
If the unit starts, you have found the problem. DO NOT leave a jumper across any safety control permanently.
If all these tests fail to isolate the problem and the code continues, check all wiring connections for tight.
At this point the IFC appears to have failed. As the most expensive part of this part of the furnace, be sure all other parts have been thoroughly checked.
Flame rollout

This is an example of flame rollout. As you can see, the flame can burn wires, damage the gas valve (center top) or cause a fire.
Flame failure code with burners lighting for a short time.

If the burners come on for 4-7 seconds then shut off, there is a problem with flame sensing. Most units will light 3 times, then go into hard lockout.
Many of the failures of modern furnaces can be traced to simple maintenance.
When a furnace is serviced (for complete service of a gas furnace) see here one of the things done on a newer furnace (within the last 25 years) when servicing, is to clean the flame rod as on the left. Symptoms of flame rod failure to sense are intermittent flame failure resulting in occasional flame failure codes on the IFC. When the power is turned off and back on, it usually starts.
As one of the attributes of the IFC is to attempt restart after 1 hour if there is a flame failure, this sometimes seems to be a very intermittent and frustrating problem to the owner.
Many parts have been replaced when the only problem is the cleanliness of the flame rod.
In some cases, if the input gas pressure is very low, there may not be enough flame to sense the flame.
If, when the burners light, not all of the burners light, there will of course be no flame sense.
If this happens, first remove the burners and clean them. If this is not effective, a thorough check of the furnace heat exchanger should be done. A carbon monoxide check should be considered. From the front of the furnace, the flame should move smoothly into the heat exchanger. Any rollout of the flame could cause flame sense problems.
Many of the failures of modern furnaces can be traced to simple maintenance.
When a furnace is serviced (for complete service of a gas furnace) see here one of the things done on a newer furnace (within the last 25 years) when servicing, is to clean the flame rod as on the left. Symptoms of flame rod failure to sense are intermittent flame failure resulting in occasional flame failure codes on the IFC. When the power is turned off and back on, it usually starts.
As one of the attributes of the IFC is to attempt restart after 1 hour if there is a flame failure, this sometimes seems to be a very intermittent and frustrating problem to the owner.
Many parts have been replaced when the only problem is the cleanliness of the flame rod.
In some cases, if the input gas pressure is very low, there may not be enough flame to sense the flame.
If, when the burners light, not all of the burners light, there will of course be no flame sense.
If this happens, first remove the burners and clean them. If this is not effective, a thorough check of the furnace heat exchanger should be done. A carbon monoxide check should be considered. From the front of the furnace, the flame should move smoothly into the heat exchanger. Any rollout of the flame could cause flame sense problems.
Location of flame rod

In this furnace, the flame rod extends into the flame from above. In a 90% efficient furnace the burners are usually on the top of the furnace section. They should also be enclosed in somewhat air tight box.
When the burners light, the flame rod senses the flame by flame rectification. The flame rod is simply a stainless steel rod placed in the flame.
Contaminates attach to the rod and inhibit its ability to sense.
Cleaning it with steel wool or sandpaper will bring its sensitivity back. Do not get overly aggressive when cleaning.
Reasonable care should be taken during cleaning. If the white ceramic is cracked, it will have to be replaced.
Do not bend the rod in an attempt to increase its sensitivity. This will not help and many of the rods are hardened and will break if too much tension is placed on them. Remember, there is nothing special about the rod. It is just a piece of stainless steel.
When troubleshooting for flame sense problems, the sequence should be: watch the burners light, if all burners light normally, clean the flame rod. Certainly check the wiring terminals. They should be tight. Any push on terminals that are loose should be crimped. Check the terminal where the flame rod wire is attached to the IFC. Check voltage supply. If the supply voltage supply is within 10% of the rated voltage (found on the model plate) it is ok. If all these things have been checked, consideration should be given to replacement of the IFC. The IFC is the most expensive part of this part of the furnace, and all other possibilities should be eliminated first.
The flame cleaning procedure is covered in the video below.
When the burners light, the flame rod senses the flame by flame rectification. The flame rod is simply a stainless steel rod placed in the flame.
Contaminates attach to the rod and inhibit its ability to sense.
Cleaning it with steel wool or sandpaper will bring its sensitivity back. Do not get overly aggressive when cleaning.
Reasonable care should be taken during cleaning. If the white ceramic is cracked, it will have to be replaced.
Do not bend the rod in an attempt to increase its sensitivity. This will not help and many of the rods are hardened and will break if too much tension is placed on them. Remember, there is nothing special about the rod. It is just a piece of stainless steel.
When troubleshooting for flame sense problems, the sequence should be: watch the burners light, if all burners light normally, clean the flame rod. Certainly check the wiring terminals. They should be tight. Any push on terminals that are loose should be crimped. Check the terminal where the flame rod wire is attached to the IFC. Check voltage supply. If the supply voltage supply is within 10% of the rated voltage (found on the model plate) it is ok. If all these things have been checked, consideration should be given to replacement of the IFC. The IFC is the most expensive part of this part of the furnace, and all other possibilities should be eliminated first.
The flame cleaning procedure is covered in the video below.
The video below explains the electronics behind
Flame failure code with burners not coming on at all

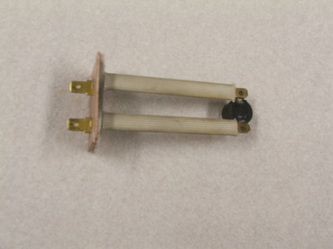
silicon carbide ignitor
On the opposite side of the burners from the flame rod (see above), will be the HSI on left. This part is charged with providing the heat for ignition of the burners.
When cycling, the inducer should start first, then the HSI should glow. then the burners should come on. If the HSI does not work, there will be no glow then you will hear a hissing sound for 4-7 seconds. Then the hissing will stop. This is the trial for ignition. because the HSI did not warm, the burners did not light and the flame was not proven. So the IFC shuts down the burners on flame safety. The above ignitor is very fragile and should be handled carefully. It is not, as some believe, ruined by being being touched, but because of its fragile nature, handling it by the black end may break it.
When cycling, the inducer should start first, then the HSI should glow. then the burners should come on. If the HSI does not work, there will be no glow then you will hear a hissing sound for 4-7 seconds. Then the hissing will stop. This is the trial for ignition. because the HSI did not warm, the burners did not light and the flame was not proven. So the IFC shuts down the burners on flame safety. The above ignitor is very fragile and should be handled carefully. It is not, as some believe, ruined by being being touched, but because of its fragile nature, handling it by the black end may break it.
A failed HSI

If the HSI does not work, there may be a white spot on it as the one on the left. This is where it is broken. All wiring leads should be checked for tight. They are also considered about to fail if they have a resistance across the leads of over 150 Ohms. This can be measured by placing a ohmmeter across the leads. If no ohmmeter is available, or you cannot use one, you can only replace it and hope.
If replacement of the ignitor does not repair the problem, it is possible that the circuit that sends power to the ignitor has failed. If the IFC is removed, it can be turned over to the trace side to look for burned spots. If a burned spot is found, it is up to you whether you try to repair it.
The video below covers trace repairs on the circuit board.
If replacement of the ignitor does not repair the problem, it is possible that the circuit that sends power to the ignitor has failed. If the IFC is removed, it can be turned over to the trace side to look for burned spots. If a burned spot is found, it is up to you whether you try to repair it.
The video below covers trace repairs on the circuit board.
Silicon nitride ignitor

This ignitor is used in the same manner as the silicon carbide ignitor. It is much tougher than the silicon carbide unit. It is not a direct replacement for a silicon carbide ignitor. To test this ignitor, the ohmmeter should read 13 to 18 ohms.
HSI mounted near burners.

This is an example of the mounting of the silicon carbide ignitor.
The silicon nitride ignitor

Here is the mounting of the silicon nitride type of ignitor.
Other codes
There are other codes such as reversed polarity which means the power for the furnace has been hooked up backwards. This would only happen upon new install or after changes have been to the wiring.
There is a shorted gas valve code code on some furnaces that that indicates the gas valve has failed and must be replaced. Gas valve setup Back to troubleshoot
There is a shorted gas valve code code on some furnaces that that indicates the gas valve has failed and must be replaced. Gas valve setup Back to troubleshoot